How Does a Zoned Heating/Cooling System Work?
August 2, 2024
Maximizing your home's comfort is our job. One way we can help you achieve this goal is through a zoned heating and cooling system. These systems allow you to heat or cool different areas of your home to the desired temperature through electronically controlled dampers in your ductwork. Keep reading to learn more about how zone heating and cooling systems work and their benefits.
What is a Zoned Heating and Cooling System?
A zoned heating and cooling system divides your home into different areas or “zones,” each controlled separately by a thermostat. Zoning your home allows for several benefits, including eliminating hot and cold spots and giving you individual control of different rooms’ temperatures.
How Does a Zoned Heating and Cooling System Work?
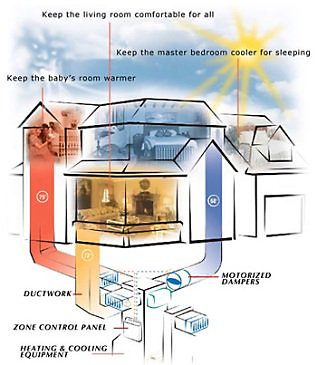
The secret to a zoned heating and cooling system is electronically controlled dampers in your ductwork. Dampers are like valves that control the flow of heated and cooled air throughout your home.
The second part of a zoned heating and cooling system is the thermostat. A thermostat is placed in each zone to control the electronic dampers in the air ducts.
When an area needs more air from your heater or air conditioner, the thermostat tells the damper to open and let more air through. Likewise, when an area has reached its desired temperature, the dampers close and send the air to the rest of your home.
Benefits of Zoned Heating and Cooling
There are several reasons Northern California homeowners zone their heating and cooling systems.
More even temperature distribution
The most common use of a zoned system is to eliminate hot and cold spots. For example, most two-story or multi-level homes suffer from uneven heating and cooling. Because heat rises, the upper levels are always warmer than the lower levels.
To combat this, you can install at least two heating zones – one upstairs and one downstairs. As one zone reaches the desired temperature, the thermostat slows the flow of air to that zone, which forces more air to the other zone and creates more even temperatures throughout your home.
Different comfort levels for different family members
Another common use of a zoned home heating and cooling system is to meet the temperature demands of different family members without fighting over the thermostat.
A zoned system lets you control the temperature of each area independently. If someone in your home likes it much colder or warmer than the rest of the household, this can be an ideal solution. A zone is installed in their bedroom, letting them change their temperature without affecting the rest of your home.
Zoning your home heating and cooling system can provide a multitude of benefits. For more information, ask one of our experts!

Drawbacks and Considerations of Zoned Heating and Cooling
Before installing a zoning system for HVAC, it’s important to consider the following factors:
Cost: Zoned heating and cooling systems are often a more significant investment than traditional systems due to the additional components and ductwork that need to be installed. However, they cool your home much more efficiently, resulting in long-term savings on your energy bills.
Maintenance: These systems feature more components and ductwork, so there is a higher chance of something going wrong. It’s essential to stay up to date on regular maintenance to ensure your system is working correctly and prevent a breakdown.
Compatibility: Converting some HVAC systems to a zoned system may be challenging. Older homes and those without ductwork are not compatible with zoned systems without significant modifications.
Is a Zoned Heating and Cooling System Right for Your Home?
We recommend zoned cooling and heating for those who live in large or multi-level homes. Multi-level homes or those with high ceilings often see heat rise, which can cause uncomfortable temperatures on the upper levels. A zoned heating system allows you to set different temperatures upstairs and downstairs to prevent temperature fluctuations.
Suppose you have a large home with rooms you don’t visit frequently. A zoned system can save you energy costs by turning off the heating and cooling in these rooms. You can also adjust each area of your home to a comfortable temperature.
Types of Zoned Thermostats
There are various types of zoned thermostats to choose from, including:
Traditional zoned systems
Wireless zoned systems
Hydronic systems
Hybrid systems
Each type of system offers various benefits and is best suited for different layouts, preferences, and homes. Contact one of our experts to learn more about which zoned system is suitable for your home.
Call Service Champions for Zoned Heating & Cooling Installation
At Service Champions, we’re dedicated to providing the best home heating, cooling, and air quality services to residents in the East Bay, San Jose, Sacramento, and surrounding areas. Whether you’re looking to install, replace, or tune up your HVAC system, our team of experts can help.
Call or book online to schedule your service today. Make sure to ask about our flexible financing options and Maintenance Value Plan. MVP members receive scheduled HVAC maintenance services, exclusive discounts, priority scheduling, and more!
Frequently Asked Questions
Is a zoned system compatible with my existing HVAC equipment?
Zone heating and cooling systems typically require two-stage or variable-capacity furnaces and air conditioners. If you’re unsure if your current HVAC equipment is compatible, contact one of our team members. We’ll assess the equipment in your home and create an estimate for zoned system installation.
How does zoning affect the efficiency of my HVAC system?
Zoned HVAC systems allow you to heat or cool only the desired areas within your home, offering increased efficiency. Unused or infrequently visited areas do not waste energy, lowering your cost and usage.
How do zoned HVAC systems differ from traditional systems?
Zoned HVAC systems differ from traditional systems as they offer controlled heating and cooling to individual zones within the house. Traditional systems treat the whole home as a zone and have one thermostat that controls the overall temperature. Zoned systems can change the temperature of an individual zone, without affecting the rest of the home.
